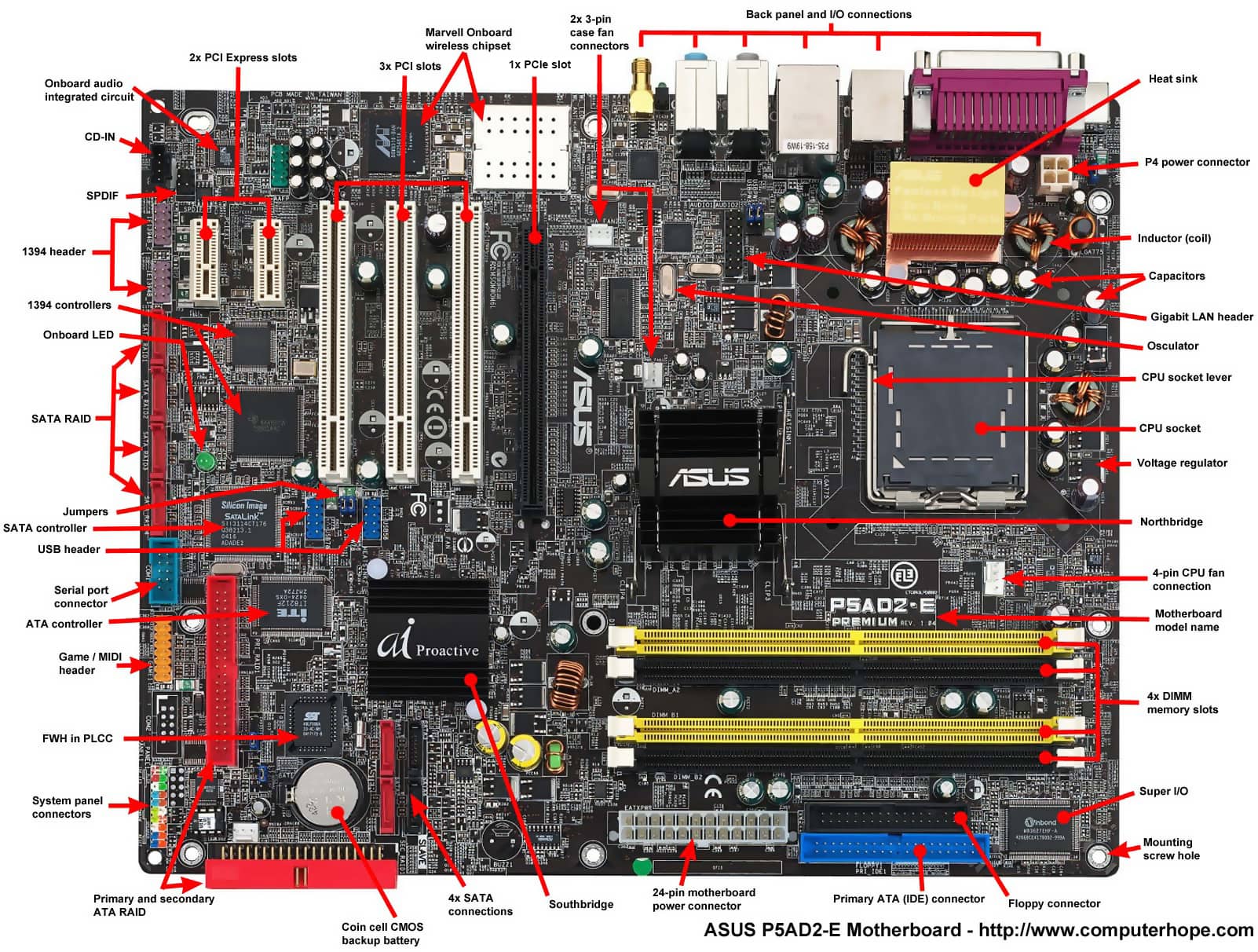
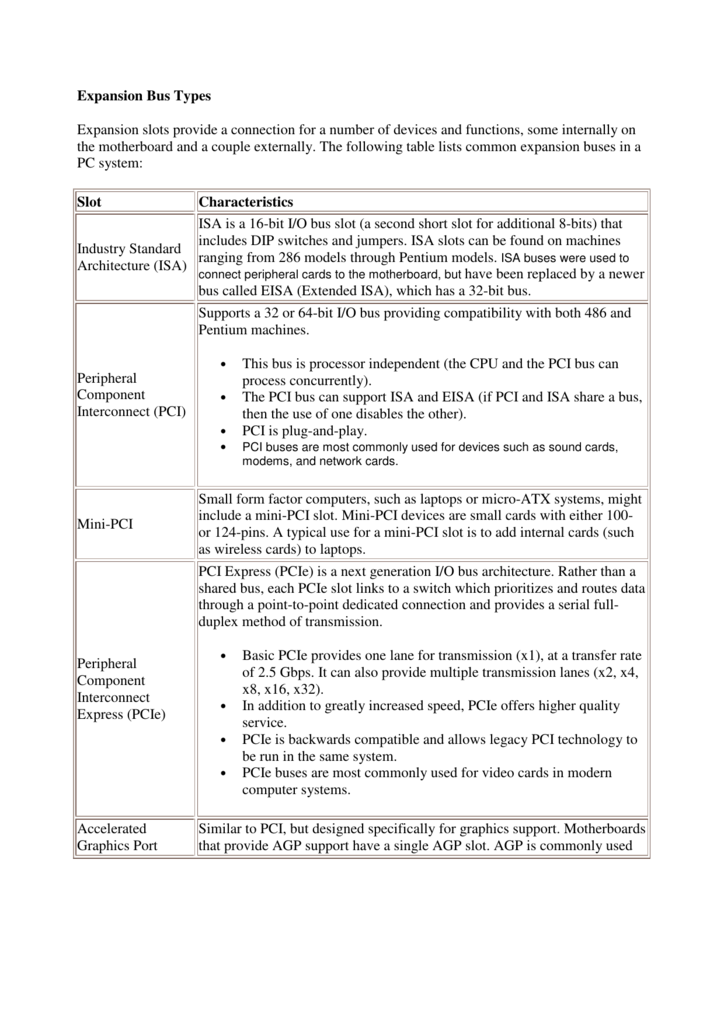
Different Expansion Slots
An expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card. An adapter card, sometimes called an expansion card, is a circuit board that enhances functions of a component of the system unit and/or provides a connection to a peripheral. A sound card enhances the sound-generating capabili-ties of a personal computer. PCI-X expansion slots were developed after PCI expansion slots, but are backward compatible with them. They're most often used in servers, rather than in desktop computers. Motherboards that use PCI-X usually contain multiple PCI slots - which may be 32-bit or 64-bit slots - that run at different speeds. M.2 is a slot that can interface with SATA 3.0 (the cable that’s probably connected to your desktop PC’s storage drive right now), PCI Express 3.0 (the default interface for graphics cards and other major expansion devices), and even USB 3.0.
PC Card Slot Types
Expansion Slots. Expansion slots, as the name suggests, are used to expand of insert Sound Card, WiFi card or a network card, and VRAM. Below you will find different expansion slots described. These were the oldest expansion slots in the history of Motherboards. They were found in AT boards and are identified by black color. All you need is Expansion Slots Different Types a smartphone that gives you Internet access via 3G, 4G, LTE, or Wi-Fi. We have listed for you some of the top mobile casinos around. They are Expansion Slots Different Types all compatible with the Android and iPhone mobile platforms, and there are some that are even Expansion Slots Different Types.
- ISA
- AGP
- PCI
- PCI-X
- PCI-E (PCIexpress)
ISA
What Are The Different Expansion Slots Available How Many For Each
ISA, or Industry Standard Architecture, is an 8bit or 16bit parallel bus system that allowed up to 6 devices to be connected to a PC. Virtually all IBM-compatible PCs made before the Pentium were based on the ISA (IBM's PC AT) bus. This asynchronous bus architecture uses 16-bit addresses and an 8-MHz clock and handles a maximum data throughput of 2 MB/s to 3 MB/s.
ISA is the precursor to PCI. Standing for 'Industry Standard Architecture' It was common from the early 1980s to the mid 1990s. ISA was a typically inelegant solution for the time, and required one to know exactly what one was doing- PnP was rare, even for so called 'ISA PnP' peripherals. In the end, the combination of flexibility, ease of use, and greater capability allowed PCI to supersede ISA.
PCI
The PCI bus architecture is a processor-independent bus specification that allows peripherals to access system memory directly without using the CPU. Not only does this free up the CPU to service other application calls, but PCI users also can simultaneously acquire data to memory and analyze existing data in real time, all while communicating with other functions on the network.
More importantly, PCI peripherals running asynchronously can send data along the 32-bit bus at a rate of up to 132 MB/s or 66 MS/s.
AGP
The Accelerates Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard. It was created in 1997 yet by 2004 was largely replaced by PCI Express. The primary advantage of AGP over PCI is that it provides a dedicated pathway between the slot and the processor rather than sharing the PCI bus. In addition to a lack of contention for the bus, the point-to-point connection allows for higher clock speeds. AGP also uses sideband addressing, meaning that the address and data buses are separated so the entire packet does not need to be read to get addressing information. This is done by adding eight extra 8-bit buses which allow the graphics controller to issue new AGP requests and commands at the same time with other AGP data flowing via the main 32 address/data (AD) lines. This results in improved overall AGP data throughput.
PCI-X
PCI-X stands for 'PCI-eXtended'. PCI-X is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and uses the same protocol.[1] It has itself been replaced in modern designs by the similar-sounding PCI Express, which features a very different logical design, most notably being a 'narrow but fast' serial connection instead of a 'wide but slow' parallel connection.
PCI-X revised the conventional PCI standard by doubling the maximum clock speed (from 66 MHz to 133 MHz)[1] and hence the amount of data exchanged between the computer processor and peripherals. Conventional PCI supports up to 64 bits at 66 MHz (though anything above 32 bits at 33 MHz is only seen in high-end systems) and additional bus standards move 32 bits at 66 MHz or 64 bits at 33 MHz. The theoretical maximum amount of data exchanged between the processor and peripherals with PCI-X is 1.06 GB/s, compared to 133 MB/s with standard PCI. PCI-X also improves the fault tolerance of PCI allowing, for example, faulty cards to be reinitialized or taken offline.
PCI Express
Types Of Computer Expansion Slots
PCIe, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP standards. PCI Express is used in consumer, server, and industrial applications, as a motherboard-level interconnect (to link motherboard-mounted peripherals) and as an expansion card interface for add-in boards. A key difference between PCIe and earlier buses is a topology based on point-to-point serial links, rather than a shared parallel bus architecture.
Bandwidth
Below is a table showing the different buses/card slot types and their maximum bandwidths:
| PCI | 132 MB/s |
| AGP 8X | 2,100 MB/s |
| PCI Express 1x | 250 [500]* MB/s |
| PCI Express 2x | 500 [1000]* MB/s |
| PCI Express 4x | 1000 [2000]* MB/s |
| PCI Express 8x | 2000 [4000]* MB/s |
| PCI Express 16x | 4000 [8000]* MB/s |
| PCI Express 32x | 8000 [16000]* MB/s |
| USB 2.0 (Max Possible) | 60 MB/s |
| IDE (ATA100) | 100 MB/s |
| IDE (ATA133) | 133 MB/s |
| SATA | 150 MB/s |
| SATA II | 300 MB/s |
| Gigabit Ethernet | 125 MB/s |
| IEEE1394B [Firewire 800] | ~100 MB/s* |
* Note - Since PCI Express is a serial based technology, data can be sent over the bus in two directions at once. Normal PCI is Parallel, and as such all data goes in one direction around the loop.
Learning with Cisco Netacad, there are many exams and lab activities to do. Some instructor require students to complete all Chapter exams, Pre-Test, Practices Final, Final Exam and Chapter Quiz. No mater what instructors want you to do, premiumexam.com offers all exams and lab activities answers and solutions with clear explanation. Our Experts have verified all exam answers before we published to the website. We recommended you to chose any relevant chapter from the following:
| IT Essentials v6.0 | |||
| Assignments | Practice Quizzes | ||
| Answers | Online | Answers | Online |
| Chapter 3 Exam | Online | Chapter 3 Quiz | Online |
| Next Chapter | |||
| Chapter 4 Exam | Online | Chapter 4 Quiz | Online |
| Lab Activities Answers & Solution | |||
| 3.1.1.3 Lab – Install the Power Supply Answers | |||
| 3.1.2.6 Lab – Install the Motherboard Answers | |||
| 3.1.3.3 Lab – Install the Drives Answers | |||
| 3.1.4.4 Lab – Install Adapter Cards Answers | |||
| 3.1.5.5 Lab – Install Internal Cables Answers | |||
| 3.1.5.8 Lab – Install Front Panel Cables Answers | |||
| 3.1.5.12 Lab – Complete the Computer Assembly Answers | |||
| 3.2.2.8 Lab – Boot the Computer Answers | |||
| 3.3.1.6 Lab – BIOS File Search Answers | |||
| 3.3.3.2 Lab – Upgrade Hardware Answers | |||
- PCIe
- AGP
- SATA
- PCI
Explanation:
The PCIe, or PCI Express, bus has four types of expansion slots with varying lengths: x1, x4, x8, and x16.
Difference Between Expansion Slots
For All Questions: IT Essentials Chapter 3 Exam Answers 2018 2019 Version 6.0 100%
Learning with Cisco Netacad, there are many exams and lab activities to do. Some instructor require students to complete all Chapter exams, Pre-Test, Practices Final, Final Exam and Chapter Quiz. No mater what instructors want you to do, premiumexam.com offers all exams and lab activities answers and solutions with clear explanation. Our Experts have verified all exam answers before we published to the website. We recommended you to chose any relevant chapter from the following:
What Are Pci Expansion Slots
| IT Essentials v6.0 | |||
| Assignments | Practice Quizzes | ||
| Answers | Online | Answers | Online |
| Chapter 3 Exam | Online | Chapter 3 Quiz | Online |
| Next Chapter | |||
| Chapter 4 Exam | Online | Chapter 4 Quiz | Online |
| Lab Activities Answers & Solution | |||
| 3.1.1.3 Lab – Install the Power Supply Answers | |||
| 3.1.2.6 Lab – Install the Motherboard Answers | |||
| 3.1.3.3 Lab – Install the Drives Answers | |||
| 3.1.4.4 Lab – Install Adapter Cards Answers | |||
| 3.1.5.5 Lab – Install Internal Cables Answers | |||
| 3.1.5.8 Lab – Install Front Panel Cables Answers | |||
| 3.1.5.12 Lab – Complete the Computer Assembly Answers | |||
| 3.2.2.8 Lab – Boot the Computer Answers | |||
| 3.3.1.6 Lab – BIOS File Search Answers | |||
| 3.3.3.2 Lab – Upgrade Hardware Answers | |||